The topstep of funded traders is APEX TRADER FUNDING
There are dozens of prop firms but none that have made it to the top like APEX.
New to investing? Understand your options!
Using a proprietary trading (prop) firm as a new retail investor can offer several benefits and opportunities, but it’s essential to understand the pros and cons before making a decision. Here are some reasons why a new investor might choose to use a prop firm to trade:
Benefits
- Leverage and Capital Access:
- Prop firms provide access to significant capital, allowing traders to control larger positions than they could with their own funds. This can enhance profit potential.
- Reduced Personal Risk:
- Trading with a prop firm means you risk less of your own capital. The firm typically absorbs the majority of the risk, although you might need to contribute a smaller amount for training or account setup.
- Education and Mentorship:
- Many prop firms offer extensive training programs, mentorship, and resources to help new traders develop their skills and strategies. This can be invaluable for someone just starting out.
- Professional Environment:
- Being part of a prop firm allows you to trade in a professional environment with access to advanced trading tools, software, and data. This can improve your trading efficiency and decision-making.
- Performance-Based Rewards:
- Successful traders can earn substantial payouts based on their performance. This merit-based system can be motivating and rewarding.
Drawbacks
- Profit Split:
- Prop firms typically take a significant share of your trading profits. The profit split can vary, but it means you’ll take home less than if you were trading independently.
- Pressure to Perform:
- Trading with a prop firm can be high-pressure, as you need to meet performance targets to maintain your position and access to capital.
- Restrictions and Rules:
- Prop firms often have strict rules and guidelines traders must follow. This can limit your trading style or strategies.
- Initial Costs:
- Some prop firms require an upfront fee for training, software, or account setup. This can be a barrier for some new traders.
- Commitment:
- Prop firms may require a significant time commitment, which could be challenging for those with other responsibilities or commitments.
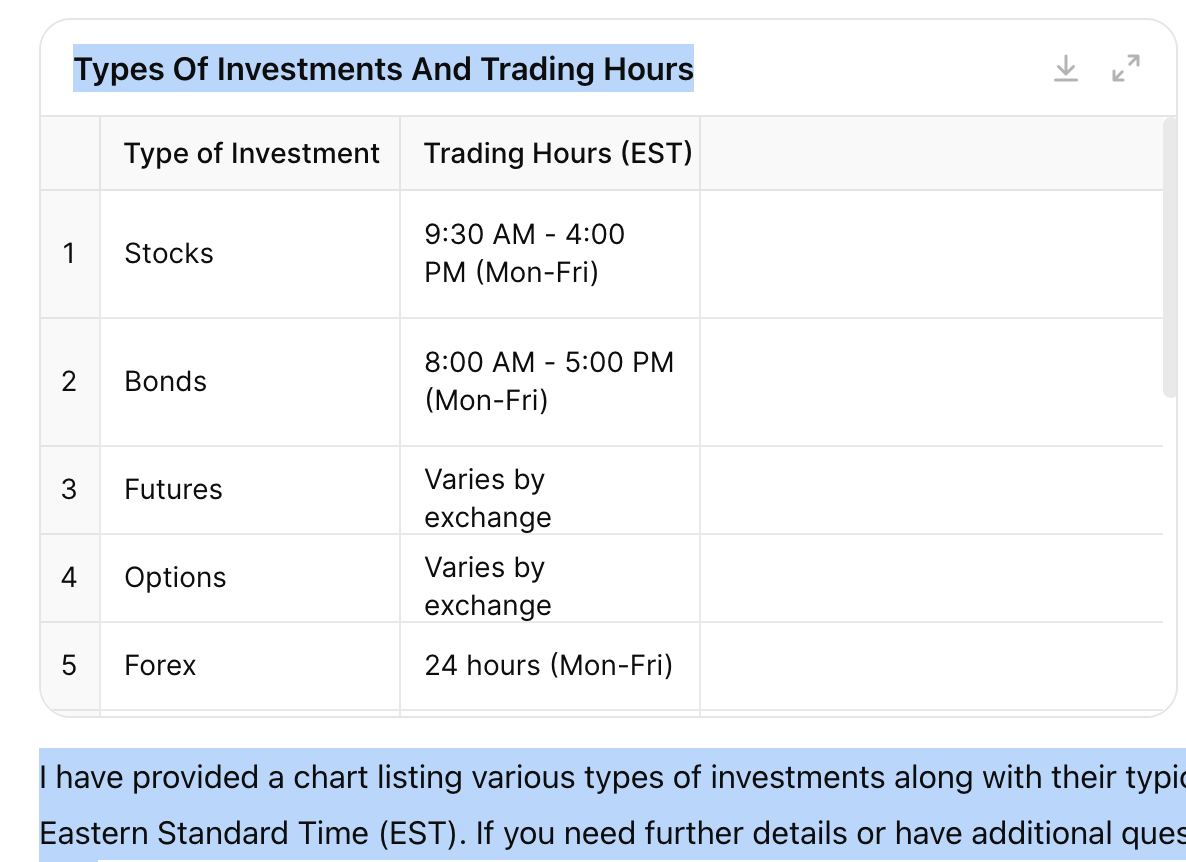
Types of investments from the topstep of traders
Types Of Investments And Trading Hours
How much money can a new investor make using a prop firm?
“The process may be confusing at first, but within a few hours, you will start to understand.”
Actual results may vary for each member, but the author of this article has passed 2 prop firm accounts.
Prop Account #1 : ( PROFIT $1637.80) It took about 10 hours to get to know the process, and I traded for 1 hour a day for about 6 days and passed.
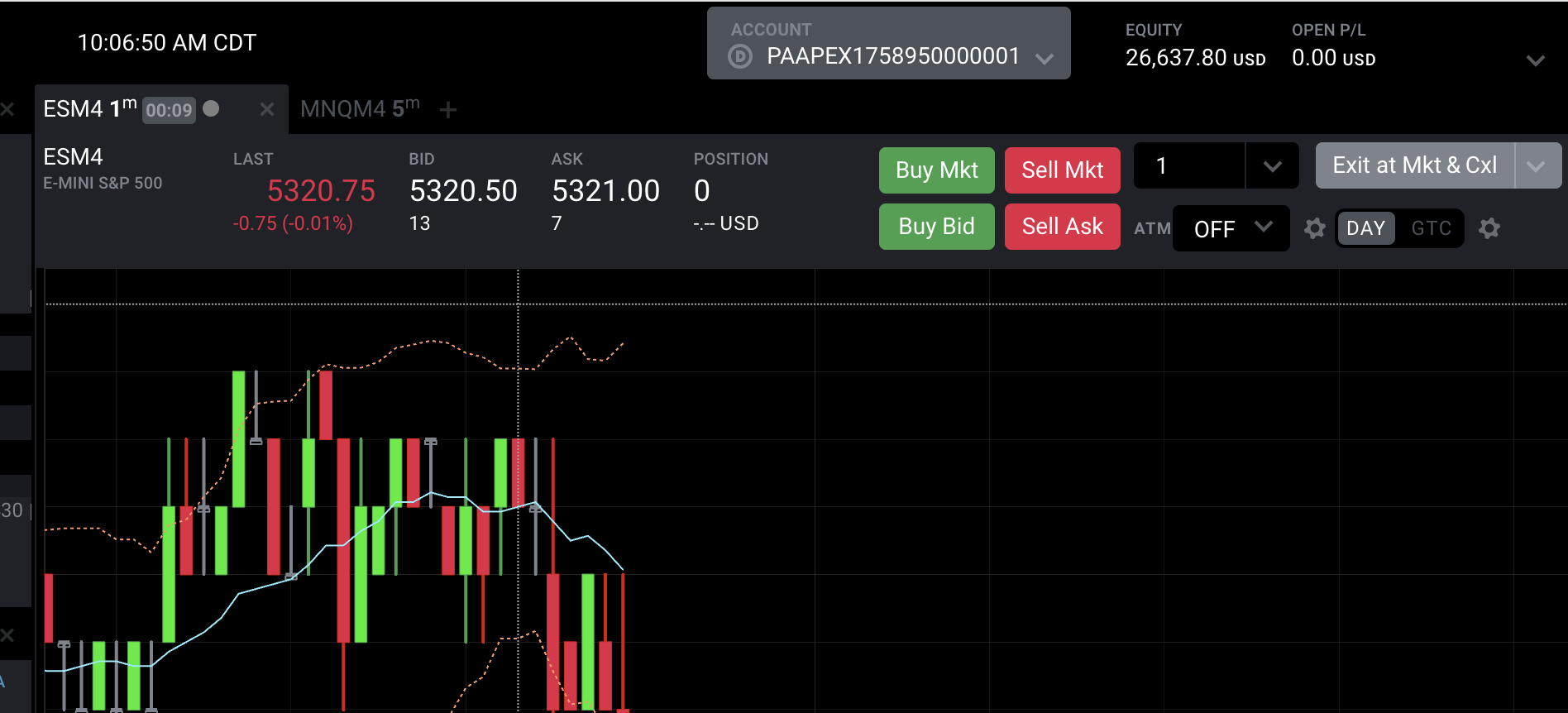
At this point I realized 2 things:
- You can request deposits at certain times of the month, so I stopped trading in this account to ensure I was able to keep my profit and started a larger account that would allow for a higher profit withdraw and allow me to keep trading. (total out of pocket at this point $87.00) Using a Funded Trader Coupon to get discount!
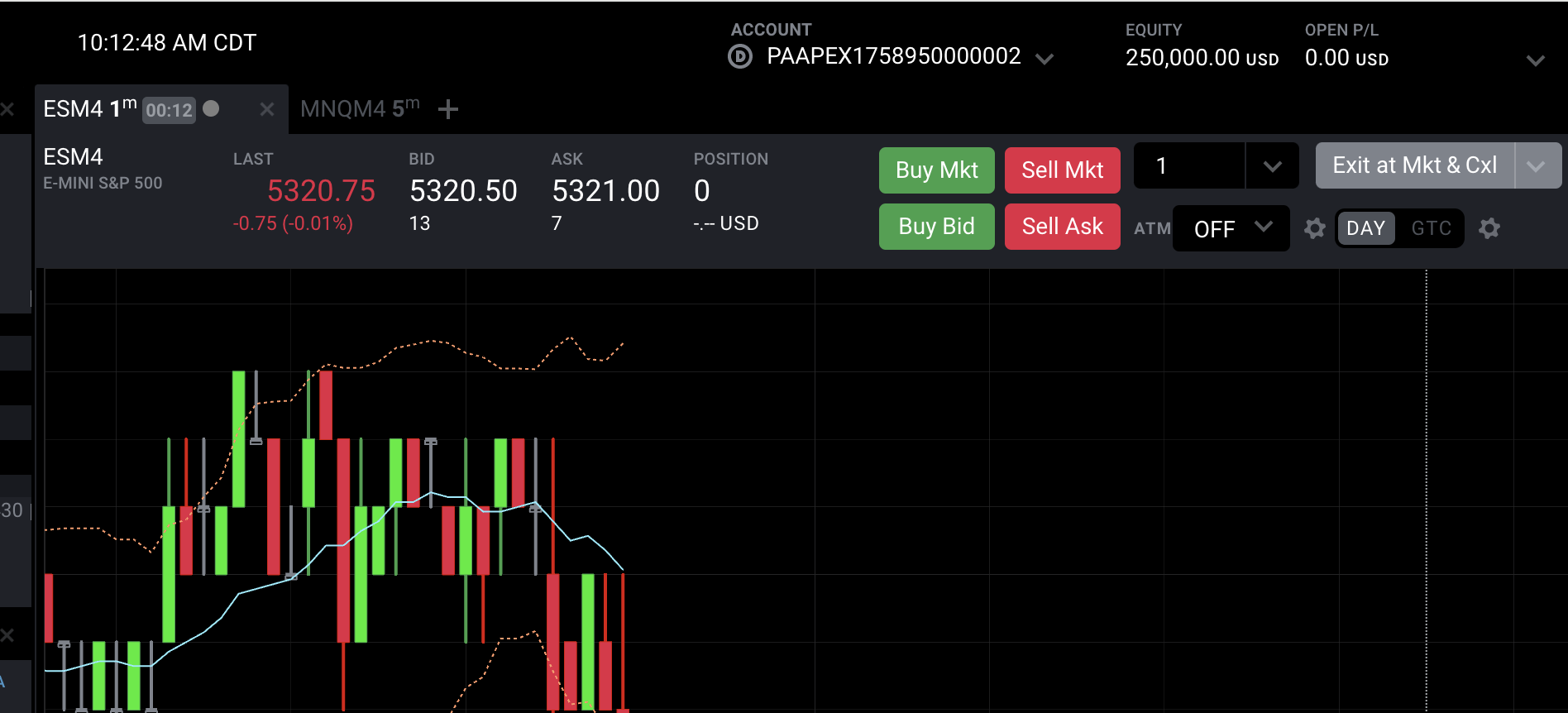
- So I thought it was easy and blew 3 accounts (cost $120.00) Added a 5th account, and passed so. had to pay $100.00 to convert.
I now have over $1600 coming to me, and have spent about $350.00 with 2 accounts to take profit from.
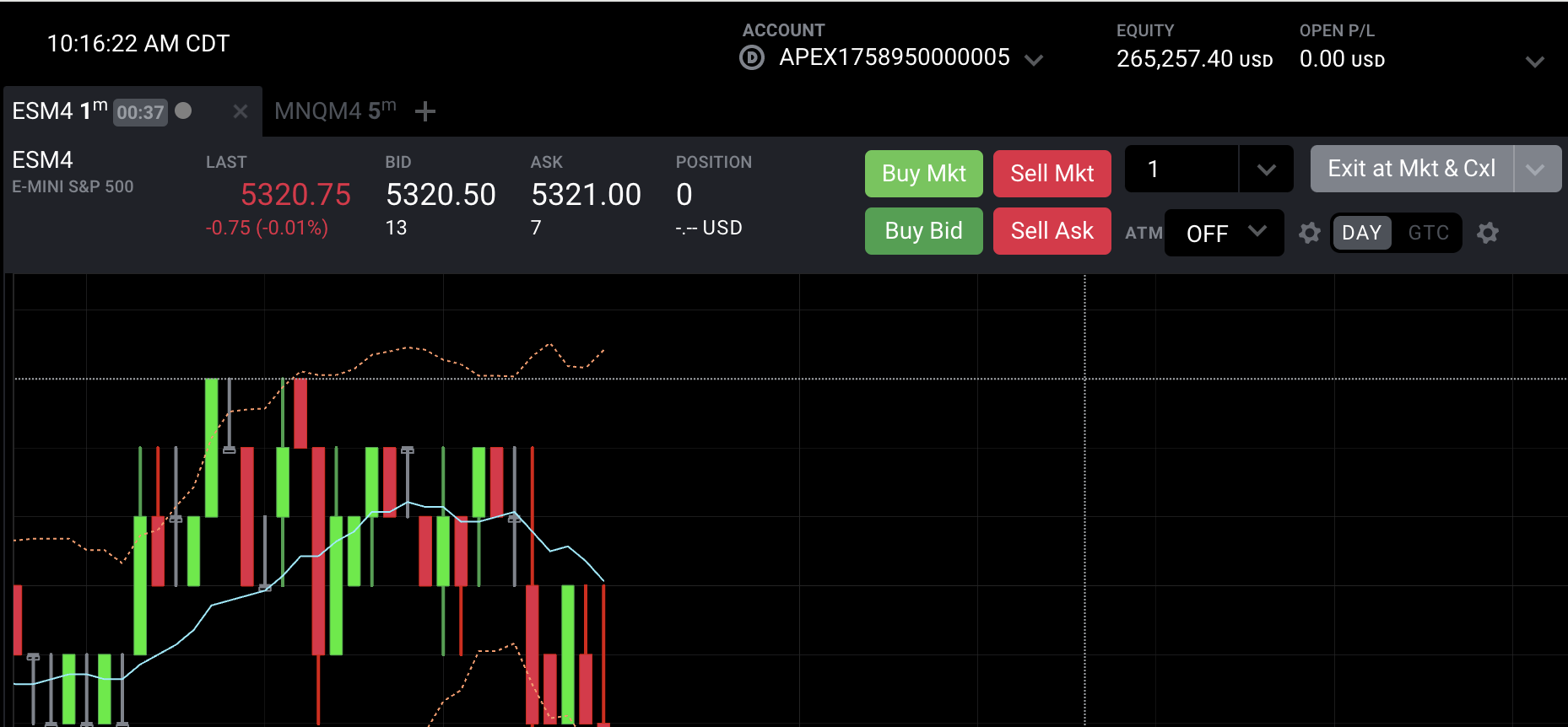
Trader Profit Training Account $15,257 ( I now have confidence in the process, making over $15k in 10 days) in an eval account that has turned into a PA account that will allow me to take $6k a month!
Goal: $15k a month PART-TIME
This is after about 40 hours of working in the first 40 days, now have not only the confidence but the tools to make over $150k a year working part time!
Just broke $12k in profit in an eval account….I have started another account to allow for more profit (close to passing in less than 10 days)
Day Trader increase in Profit $28,883.08 in P&L increaase in under 30 days for under $300.00 out of pocket!
Conclusion
For a new investor, joining a prop firm can be a double-edged sword. The access to capital, training, and professional environment can accelerate learning and potentially lead to higher profits. However, the pressure, profit splits, and potential costs are important factors to consider. It’s crucial to thoroughly research different prop firms, understand their terms, and assess whether the environment and conditions align with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Why is day trading one of the fastest-growing side hustles?
Why Day Trading with a Prop Firm is Perfect for Part-Time Work and Flexible Hours
In today’s fast-paced world, the allure of flexible work hours and the potential to earn a substantial income draws many to consider day trading as a side hustle. For those looking to dive into this exciting world, partnering with a proprietary trading (prop) firm can be an ideal way to start. Here’s why day trading with a prop firm is an excellent fit for people seeking part-time work with the potential to make full-time money.
1. Access to Capital
One of the most significant barriers to entry in day trading is the substantial capital required to make meaningful trades. Prop firms provide traders with access to their capital, allowing you to trade larger positions than you could with your own funds. This access can significantly enhance your profit potential without risking a large amount of your own money.
2. Comprehensive Training Programs
Many prop firms offer extensive training programs tailored to new traders. These programs cover the fundamentals of trading, advanced strategies, risk management, and the use of trading platforms. Learning from experienced traders and having access to professional resources can accelerate your learning curve, giving you the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the markets.
3. Flexible Trading Hours
Day trading offers flexibility that is hard to find in traditional jobs. Depending on the markets you trade (stocks, forex, futures), you can choose trading hours that fit your schedule. Prop firms often provide access to multiple markets, enabling you to trade at different times of the day. This flexibility makes it possible to balance trading with other commitments, making it an ideal side hustle.
4. Lower Personal Financial Risk
When trading with a prop firm, you are primarily using the firm’s capital. While you may need to deposit a small amount to get started, your personal financial risk is significantly lower than trading independently. The firm absorbs most of the financial risk, allowing you to focus on developing your trading strategies without the fear of losing a significant portion of your own money.
5. Performance-Based Rewards
Prop firms operate on a performance-based model, meaning your income is directly tied to your trading success. High-performing traders can earn substantial payouts, often much higher than what is possible in traditional part-time jobs. This merit-based system can be highly motivating, encouraging you to continually improve your skills and strategies.
6. Access to Advanced Tools and Technology
Prop firms provide their traders with state-of-the-art trading platforms, real-time data feeds, and advanced analytical tools. These resources are often too expensive for individual traders but are crucial for making informed trading decisions. With these tools at your disposal, you can enhance your trading performance and gain a competitive edge in the market.
7. Mentorship and Community Support
Being part of a prop firm means you are not trading alone. You have access to a community of traders and mentors who can provide guidance, share strategies, and offer support. This collaborative environment can be incredibly beneficial, especially for new traders looking to learn from more experienced professionals.
8. Scalability
As you gain experience and demonstrate consistent profitability, prop firms often increase the amount of capital available to you. This scalability means your potential earnings can grow significantly over time. What starts as a part-time side hustle can evolve into a highly lucrative career.
Conclusion
Day trading with a prop firm offers a unique blend of flexibility, education, and financial opportunity that is ideal for those looking to earn full-time money on a part-time schedule. The combination of access to capital, comprehensive training, and a supportive trading environment makes prop firms an excellent starting point for aspiring traders. Whether you’re looking to supplement your income or eventually transition into full-time trading, partnering with a prop firm can provide the resources and support needed to achieve your financial goals.

















